CSE Helper
Powered By Dream Dragon Creation
Single Linked List
Introduction
A linked list is a data structure in which the objects are arranged in a linear order. Unlike an array, however, in which the linear order is determined by the array indices, the order in a linked list is determined by a pointer in each object. Linked lists provide a simple, flexible representation for dynamic sets.
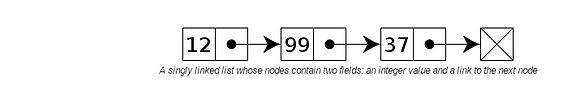
here are som of the basic operations on a singly Linked List
1. Creating a new List
2. adding new elements
3. Traversing a List
4. Printing a List
5. Deleting a elements
basic funtions to perform the above techniques hava been defined in the code below.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
CREATING A NEW LIST
a new Linked List cration means that we do not have any elements in the list and we want to start fresh. This means allocating space in the memory for a node and then inserting data into it.
Since only a single node is created the NEXT of the node will always be Null.
1. struct node* createList(struct node*head, int number){
2. struct node*temp= (struct node*) mallac(size of(struct node));
3. temp-> data= number;
4. temp-> next = NULL;
5. head = temp;
6. return head;
7. }
_______________________________________________________________________________________
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS
we can add new elements to the end of the Linked List as default case. As well as we can insert in between beginning at a later stage.
.
LIST-INSERT ( L , x )
Inserts the node x into the front of the list L
Extensions
LIST-INSERT ( L , x , i )
Inserts the node x into the i th location of the list L
_______________________________________________________________________________________
TRAVERSING A LIST
A linked List traversal is very easy. The Head of the list always points to the first element of the linked list. if we do a statement like
.
HEAD = HEAD -> next
we can move to the next node.
a Linked List, ends we encounter a NULL, so basically, if we keep on performing the NEXT operation until we encounter a NULL, that means we have successfully traversal the linked list.
.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Sourse code Implement in C
1. #include<stdio.h>
2. #include<stdlib.h>
3. typedef struct Node
4. {
5. int data;
6. struct Node *next;
7. } node;
8. void insert(node *pointer, int data)
9. { /* Iterate through the list till we encounter the last node.*/
10. while ( pointer -> next != NULL )
11. {
12. pointer = pointer -> next;
13. }
14. /* Allocate memory for the new node and put data in it.*/
15. pointer->next = (node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( node ) ) ;
16. pointer = pointer->next;
17. pointer->data = data;
18. pointer->next = NULL;
19. }
20. int find(node *pointer, int key)
21. {
22. pointer = pointer -> next; //First node is dummy node
23. /* iterate through the entire linked list and search for the key. */
24. while ( pointer != NULL )
25. { if ( pointer -> data == key ) //key is found.
26. { return 1
27. }
28. pointer = pointer -> next ; //Search in the next node.
29. }
30. /*Key is not found */
31. return 0;
32. }
33. void delete(node *pointer, int data)
34. { /* Go to the node for which the node next to it has to be deleted */
35. while ( pointer -> next != NULL && ( pointer -> next ) -> data != data )
36. { pointer = pointer -> next;
37. }
38. if ( pointer -> next == NULL )
39. { printf ( "Element %d is not present in the list \n " , data ) ;
40. return;
41. }
42. /*Now pointer points to a node and node next to it has to be removed */
43. node *temp;
44. temp = pointer -> next;
45. /*temp points to the node which has to be removed*/
46. pointer->next = temp->next;
47. /*We removed the node which is next to pointer (which is also temp) */
48. free(temp);
49. /* Beacuse we deleted the node, we no longer require the memory used
for it . free() will deallocate the memory. */
50. Return;
51. }
52. void print ( node *pointer)
53. {
54. if ( pointer == NULL )
55. {
56. return;
57. }
58. printf ( "%d " , pointer->data ) ;
59. print ( pointer -> next ) ;
60. }
61. int main( )
62. { /* start always points to the first node of the linked list.
temp is used to point to the last node of the linked list.*/
63. node *start,*temp;
64. start = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
65. temp = start;
66. temp -> next = NULL;
67. /* Here in this code, we take the first node as a dummy node. The first node does not contain data, but it used because to avoid handling special cases in insert and delete functions. */
68. printf ( "1. Insert \n " ) ;
69. printf ( " 2. Delete \n " ) ;
70. printf ( " 3. Print \n " ) ;
71. printf ( " 4. Find \n " ) ;
72 while ( 1 )
73. { int query;
74. scanf ( " %d " , &query ) ;
75. if ( query == 1 )
76. {
77. int data;
78. scanf ( " %d " , &data ) ;
79. insert ( start , data ) ;
80. }
81. else if ( query == 2 )
82. { int data;
83. scanf ( " %d " , &data ) ;
84. delete(start,data);
85. }
86. else if ( query == 3 )
87. { printf ( "The list is " ) ;
88. print ( start -> next ) ;
89. printf ( " \n " ) ;
90. }
91. else if ( query == 4 )
92. {
93. int data;
94. scanf ( " %d " , &data ) ;
95. int status = find ( start , data);
96. if ( status )
97. { printf ( "Element Found \n " );
98. }
99. else
100. { printf ( " Element Not Found \n " )
101. }
102. }
103. }
104. }
Sourse Code implements in C++
1. #include “stdafx.h”
2. #include<iostream>
3. Using namespace std;
4. Class node{
5. Public:
6. int value; // value stored in the node
7. node *next; // pointer to next node
8. };
9. Class singleLinkedList{
10. node *head; // poiter to first node that is head
11. int size;
12. singleLinkedList ( ) {
13. head = NULL;
14. size = 0;
15. }
16. void insert ( int value ) ;
17. void insertAt ( int value , node *nodeB ) ;
18. void remoreValue ( int delValue ) ;
19. void remore ( node* nodeB ) ;
20. void printList ( ) ;
21. };
22. //insert a node
23. Void singleLinedList : : insert ( int value ) {
24. if ( head == NULL )
25. {
26. node* newNode;
27. newNode = new node();
28. head = newNode;
29. newNode -> next = NULL;
30. newNode -> value = value;
31. size = size + 1 ;
32. }else{
33. insertAt(value , head->next);
34. }
35. //insert a node after given node
36. Void singleLinedList :: insertAt ( int value , node* nodeB ) {
37. if ( nodeB == NULL ) {
38. node* newNode;
39. newNode = new node();
40. nodeB = newNode;
41. newNode->value = value;
42. size = size + 1 ;
43. }else{
44. insertAt ( value , nodeB->next);
45. }
46. }
47. //remove a node given from removevalue
48. Void singleLinkedList :: remove ( node* nodeB ) {
49. node* newNode = head;
50. if ( head == nodeB ){
51. head = head->next;
52. }else{
53. while ( ! ( newNode->next == nodeB ) ) {
54. //finding the node that want to delete
55. newNode = newNode->next;
56. }
57. newNode->next = newNode->next->next;
58. }
59. }
60. // remove value
61. Void singleLinkedList::removeValue(int delValue){
62. node* newNode = head;
63. while(!(newNode->value == delValue)){
64. newNode = newNode->next;
65. }
66. if ( ! ( newNode == NULL ) ){
67. remove(newNode); // call the delete node function
68. cout<< ” value Deleted. “<< endl;
69. }else{
70. cout<< “ value not found “ << endl;
71. }
72. }
73. // print the list
74. Void singleLinkedList :: printList( ){
75. node* curr2;
76. Curr2 = head;
77. cout << “ \n------\n” ;
78. cout << “ list : “ ;
79. Cout << " ------ \n " ;
80. While( curr2 != NULL){
81. cout<< “ | “ << curr2 ->value << “ | “;
82. cout = curr2 ->next;
83. }
84. cout<<endl;
85. }
86. Int main(){
87. singleLinkedList * st ;
88. st = new singleLinkedList ( ) ;
89. St->insert(8);
90. St->printList();
91. St->insert(5);
92. St->printList();
93. St->insert(10);
94. St->printList();
95. St->remoreValue(8);
96. St->printList();
97. St->remoreValue(54);
98. St->printList();
99. Return 0;
100. }
Sourse Code implements in Java
1. package single_Linked_list;
2. /**
3. *
4. @author cse helper
5. */
6. public class Node {
7. private Node next;
8. private int value;
9. public void setValue(int value){
10. this.value = value;
11. }
12. public void setNext ( Node next ){
13. this.next = next;
14. }
15. public int getValue ( ) {
16 return value;
17. }
18. public Node getNext ( ) {
19. return next;
20. }
21. }
22. public class Linked_List {
23. private Node head;
24. public Linked_List ( ) {
25 Node newNode = new Node();
26. head = newNode;
27. }
28. public void insert ( int value ) {
29. Node newNode = new Node ( ) ;
30. head.setValue ( value ) ;
31. newNode.setNext ( head ) ;
32. head = newNode;
33. }
34. public void print ( ) {
35. Node traversal = new Node ( ) ;
36. traversal = head.getNext ( ) ;
37. while ( true ) {
38. System.out.print ( traversal.getValue ( ) ) ;
39. System.out.print ( " " ) ;
40. // terminating condition
41. if ( traversal.getNext ( ) == null ) {
42. break;
43. }
44. traversal = traversal.getNext ( ) ;
45. }
46. System.out.println ( " " ) ;
47. }
48. public boolean delete ( int value ) {
49. Node deleteNode = new Node ( ) ;
50. deleteNode = head;
51. if ( head.getValue ( ) == value ) {
52. head = head.getNext ( ) ;
53. //delete head
54. return true ;
55. }
56. while ( true ) {
57. // terminating condition
58. if ( deleteNode.getNext ( ) == null ) {
59. System.out.println ( "value not found ! " ) ;
60. return false;
61. }
62. // cheaking next node is the delete value
63. if ( deleteNode.getNext( ).getValue( ) == value ) {
64. Node temp = deleteNode.getNext( ) ;
65. // deleting node, value between head and end
66. if ( temp.getNext( ) != null ) {
67. deleteNode.setNext ( temp.getNext( ) ) ;
68. //delete temp
69. return true;
70. }else{
71. //deleting value in last
72. deleteNode.setNext(null);
73. return true;
74. }
75. }
76. deleteNode = deleteNode.getNext ( ) ;
77. }
78. }
79. }
80. public class Main {
81. public static void main ( String[ ] args ) {
82. Linked_List list1 = new Linked_List ( ) ;
83. System.out.println ( "create list1 and insert 10,35,14 " ) ;
84. list1.insert ( 10 ) ;
85. list1.print( ) ;
86. list1.insert ( 35 ) ;
87. list1.print( ) ;
88. list1.insert ( 14 ) ;
89. list1.print( ) ;
90. System.out.println ( "delete 14" ) ;
91. list1.delete ( 14 ) ;
92. list1.print( ) ;
93. }
94. }